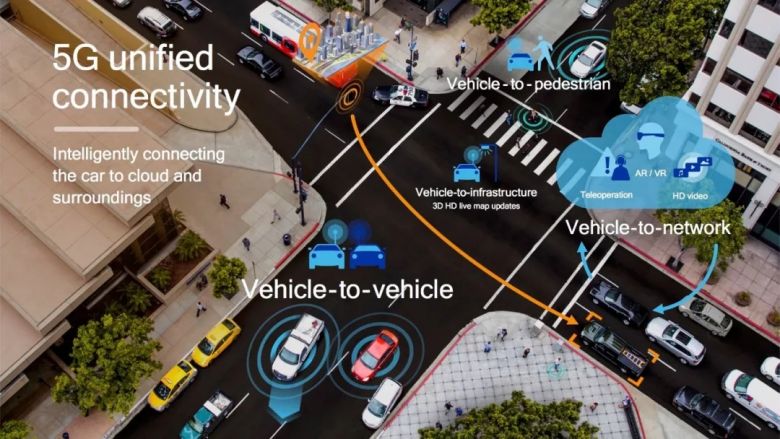
Definition of V2X
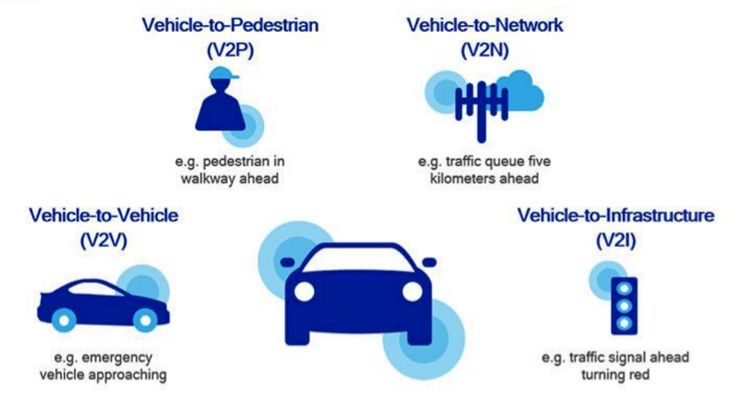
Vehicle to Everything (V2X) is a new generation of information and communication technology that connects vehicles to everything. V represents vehicles and X represents any object interacting with the vehicle. At present, X mainly includes vehicles, people, roadside infrastructure, and network. The information modes of V2X interaction include Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V), Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I), Vehicle to Pedestrian (V2P), Vehicle to Network (V2N).
V2X technologies defined by 3GPP include V2V, V2I, V2P, V2N/ V2C and other communication scenarios. Autonomous driving security leader, AUTOCRYPT, announced that its V2X security solution, Auto Crypt V2X, now implements YD/T 3957-2021, the newest standard for LTE-based V2N communications and credential managemen.
V2X uses various wireless communication technologies to connect traffic participation factors such as vehicle, road, people, cloud, etc. V2X can not only enable vehicles to obtain more perceptual information, but also promotes the innovation and application of autonomous driving technology. It is also beneficial to the construct the intelligent traffic system. It can promote the development of new models and new formats of vehicles and traffic services. And it is significant in improving traffic efficiency, saving resources, reducing pollution, reducing the frequency of accidents, and improving traffic management.
Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V)
Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) is used for vehicle-mounted communication. The most common application scenario is in urban streets and expressways. Vehicles communicate with each other, send data, realize information and data sharing in that case.
The intelligent vehicle computing platform can send or receive the following data: speed, the relative position, braking, orientation, and all data related to safety. It can even take pictures, audio, or video of things around. Then, it analyzes and forecasts other vehicles’ driving behavior. Doing so can achieve active security strategy, improve road safety, and provide data points for semi-automatic and automatic driving.
V2V technology allows vehicles to prevent accidents by relaying real-time information about themselves and the road ahead. It can reduce commuting time, and ultimately improve the traffic environment and reduce traffic congestion.
V2V vehicle communication can achieve vehicle-to-vehicle communication through D2D protocol in C-V2X. It brings another operation and maintenance mode for OEMs. Namely, it can effectively establish intelligent fleets, plan route, reduce fuel consumption, and improve operating income.
Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I)
Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I) refers to the communication between the vehicle-end unit and the roadside infrastructure, such as traffic lights, traffic cameras, and roadside units. Roadside infrastructure captures information about the surrounding area and publishes all kinds of real-time information. V2I is mainly used in real-time information service, vehicle monitoring and management, paying tolls without stopping, etc.
The intelligent vehicle computing platform needs the analysis of the warning information received from roadside infrastructure, such as blind spot collision at crossroads, road hazard, road construction, emergency vehicles, traffic jam and accident warning, as well as the traffic signal or sign recognition in blind area. The analysis can provide users with information about corresponding dangerous situation, recommendation of optimized driving behavior. This can also promote the rationalization and perfection of road vehicle driving and surrounding information.
V2I enables wireless data exchange between vehicles and roadside traffic facilities. Its main applications include intersection safety management, vehicle speed control, electronic toll collection, transportation safety management, and road construction and height limit warning. This technology will make transportation facilities smarter, including no entry lights and weather information systems. It can evolve into intelligent transportation facilities which can recognize high-risk situations and automatically take alerting measures through various algorithms.
Vehicle to People (V2P)
Vehicle to People (V2P) refers to the communication between vehicle-end units in vehicles and vulnerable traffic groups (including pedestrians and cyclists) through user devices (such as smart phones, wearable devices, bicycle GPS signalers, etc.). V2P is mainly used in traffic safety, smart keys, location information services, car sharing, etc.
The intelligent vehicle computing platform enables keyless entry and remote startup by supporting powerful secure communication and using smart keys. At the same time, the powerful computing ability can calculate the movement track of pedestrians or cyclists in real time. It can provide drivers with driving prediction and help them avoid traffic accidents.
V2P allows pedestrians and cyclists to become a node in the V2X communication environment through their smartphones. It can send or receive warning signals, such as telling on-line connected traffic lights in advance to determine whether it will take longer to cross the road. It can also prompt pedestrians to cross the road at the intersection in front of nearby vehicles, or prompt vehicles that there are bicycles riding in the adjacent lanes.
V2P communication depends primarily on the wireless communication protocol of user’s device. This requires the intelligent vehicle computing platform to support as many wireless communication protocols as possible, such as BT, WIFI, Zigbee, Z-Wave, NB-Iot/ LoRA, LTE/5G. Then it can effectively implement V2P.
Vehicle to Network/Cloud (V2N/ V2C)
Vehicle to Network/Cloud (V2N/ V2C) refers to the connection between the on-board device in a vehicle and the cloud platform through network. The cloud platform interacts with the vehicle. It also stores and processes the acquired data, and provides remote traffic information, entertainment, business services and vehicle management. V2N/ V2C is mainly applied to vehicle navigation, vehicle remote monitoring, emergency rescue, information entertainment services, etc.
For V2N/ V2C, intelligent vehicle computing platform requires powerful and fast data processing capability, and massive data storage mechanism to process network data with ultra-high speed, ultra-high throughput, high reliability, and ultra-low delay.
Undoubtedly, V2N/V2C needs to adopt the new antenna transmission technology in C-V2X, high frequency transmission, same frequency full duplex and other efficient technologies. This requires intelligent vehicle computing platforms to support new network architectures, such as the integration of D-RAN, C-RAN, D2D, MTC and other access technologies. V2N/V2C communication is achieved through various low-cost and high-speed optical transmission networks.
The Introduction of Two Big Industrialization Camp of V2X Technology
The V2X industry is divided into two standards and industry camps, DSRC and C-V2X. China’s V2X market has the world’s largest 5Gnetwork and a mature industrial chain, and it does not have much accumulation in DSRC technology. Considering factors such as avoiding patent risks, some analysts believe that China’s V2X technology development will be inclined to C-V2X.
DSRC (dedicated short-range wireless Communication standard) is based on IEEE802.11p, and V2V is its main application mode. DSRC’s biggest competitive stake is an early start. Back in 1999, the Federal Communications Commission set aside 75 MHz for V2X in the 5.9 GHz region. The United States, Europe and other countries have put forward relevant standards and specifications. After more than ten years of development history, they formed a mature industrial chain, and can be used for commercial purposes.
C-V2X, a wireless communications technology for vehicles based on cellular network. It’s a vehicle wireless communication technology based on the evolution of 4G/5G and other cellular communication technologies, including LTE-V2X and 5G-V2X. From the perspective of technology evolution, LTE-V2X supports smooth evolution to 5G-V2X. C-V2X, initiated by 3GPP, is currently at a critical stage of standard development and technology accumulation. 3GPP developed the first version of the standard in 2017 and has formed an industrial camp dominated by telecom industry chain companies such as Huawei, Qualcomm, Ericsson and Nokia, telecom operators and automotive companies.
Typical V2X application scenarios
V2X currently covers three typical application scenarios: traffic active safety, traffic efficiency and information services. And it’s developing to support the implementation of autonomous driving applications. In The Basic Application of Intelligent Connected Vehicles jointly issued by Future Mobile Communication Forum and Vehicle-mounted Information Service Industry Application Alliance, 72 kinds of intelligent connected vehicle application scenarios are defined.
The basic application scenarios include:
- Active traffic safety: Forward collision warning, left turn assist/alarm, incoming main road assist/collision alarm, intersection collision alarm (with signal light/no signal light/no visual range, etc. with roadside unit), intersection collision alarm (with signal light/no signal light/no visual range, etc. without road units), overtaking auxiliary/reverse overtaking remind/through overtaking, blind spot alerting/auxiliary lane changing, emergency brake alerting (emergency electronic brake lights), vehicle safety function is out of control alarm, abnormal vehicle alarm (including static/slow vehicles ahead), stationary vehicles remind (such as traffic accident, vehicle failure cause), non-motor vehicles (electric cars, Bicycle, etc.) crossing alerting /pedestrian crossing alerting, emergency vehicle alerting, slippery/dangerous road alerting (wind, fog, ice, etc.), red light (/ yellow light) alarm).
- Traffic efficiency: deceleration zone/speed limit reminder (tunnel speed limit, general speed limit, curve speed limit, etc.), speed guidance, car signs, electronic charging without parking.
- Information services: entrance payment, automatic parking guidance and control, SOS/eCALL service, vehicle theft/damage (including whole vehicles and parts) alarm, remote vehicle diagnosis, maintenance tips.
Introduction of Vehicle Wireless Communication Technology C-V2X based on Cellular Network Communication Technology
C-V2X Communication Interface
C-V2X includes two types of communication interfaces: one is a short distance direct communication interface (PC5) between vehicles, people, and roads. The other one is the communication interface (Uu) between terminals and base stations, which enables reliable communication over long distances and a larger range. C-V2X direct communication provides extended communication range and enhanced reliability without relying on cellular network assistance or coverage.
Network communication (Uu interface), using LTE broadcasting, is relayed on V2X servers to send information to another node. LTE wireless base stations are used to assist V2V data scheduling and interface management. The Uu interface has broad coverage and can be sent back to the cloud platform. It’s suitable for infotainment, long-distance road hazards or traffic conditions, delay tolerance of safety messages and other similar business types.
Direct communication (PC5 interface) is based on D2D (Device-to-Device) adjacent communication service in LTE standard. The PC5 interface enables high speed and high-density communication at 250Kph, supporting communication without LTE network coverage. LTEV2X supports simultaneous time synchronization between base station and global navigation satellite system (GNSS). It allows users to broadcast messages directly to each other with or without network coverage. PC5 interface has the characteristics of low delay and small coverage, which is suitable for traffic safety and local traffic efficiency services.
Standardization progress of V2X
The standardization of C-V2X:
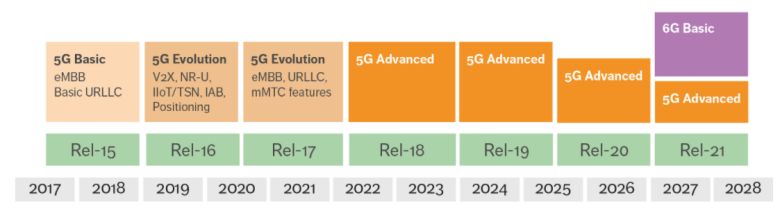
- The path toward 5G Advanced begins with Rel-17, which includes significant enhancements to several radio access network (RAN) functionalities that are already deployed in live New Radio (NR) networks. The primary aim of Rel-17 is to improve 5GS performance, support new use cases and verticals, and provide ubiquitous connectivity in different deployment conditions and scenarios.
- The 3GPP RAN standardization team began discussing the scope of Rel-18 in June 2021 at the 3GPP RAN Rel-18 Workshop and aims for approval of the detailed scope by December 2021. Rel-18 introduces further intelligence into wireless networks by implementing machine-learning-based techniques at different levels of the network.
Ecotron
Ecotron’s latest generation ADCU, EAXVA05, is an intelligent computing platform designed specifically for autonomous driving systems. EVXVA05 is equipped with 2 NVIDIA Xavier chips and 1 Infineon TC297 chip. With basic software and development tools, developers can safely, conveniently, and efficiently build low-speed L4-level autonomous driving systems in confined areas. NVIDIA designs Xavier particularly for embedded intelligent systems. Xavier supports autonomous driving functions such as sensor fusion, environment perception, and path planning. Infineon TC297 has a TriCore™ architecture and has an operating frequency of 300MHz. Moreover, it has 728KB + 8MB capacity and ECC (error correction coding) RAM protection. Ecotron’s ADCU is designed based on the ISO26262 standard and supports ASIL-D safety level requirements. Engineers can develop vehicle control and functional safety-related strategies based on this MCU.



